Loading UI and Streaming 加载 UI 和流式传输
The special file loading.js helps you create meaningful Loading UI with React Suspense. With this convention, you can show an instant loading state from the server while the content of a route segment loads. The new content is automatically swapped in once rendering is complete.
特殊文件 loading.js 帮助您使用 React Suspense 创建有意义的加载 UI。通过此约定,您可以在路由段内容加载时从服务器显示即时加载状态。一旦渲染完成,新内容将自动交换。
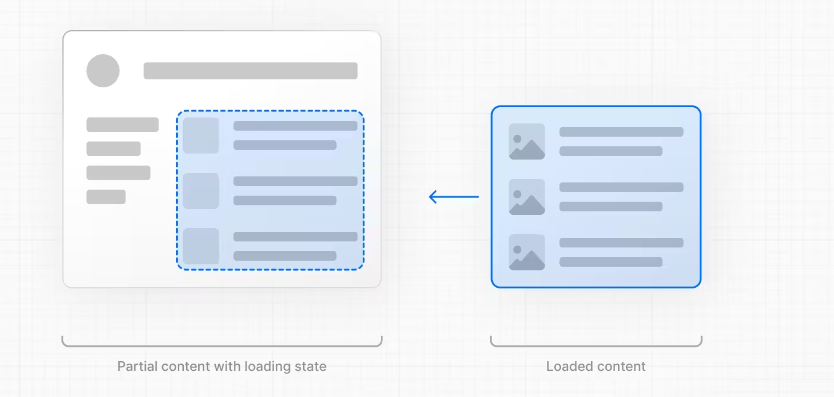
1.Instant Loading States 即时加载状态
An instant loading state is fallback UI that is shown immediately upon navigation. You can pre-render loading indicators such as skeletons and spinners, or a small but meaningful part of future screens such as a cover photo, title, etc. This helps users understand the app is responding and provides a better user experience.
即时加载状态是导航后立即显示的备用 UI。您可以预渲染加载指示器,例如骨架和旋转器,或未来屏幕的一小部分有意义的部分,例如封面照片、标题等。这有助于用户了解应用程序正在响应并提供更好的用户体验。
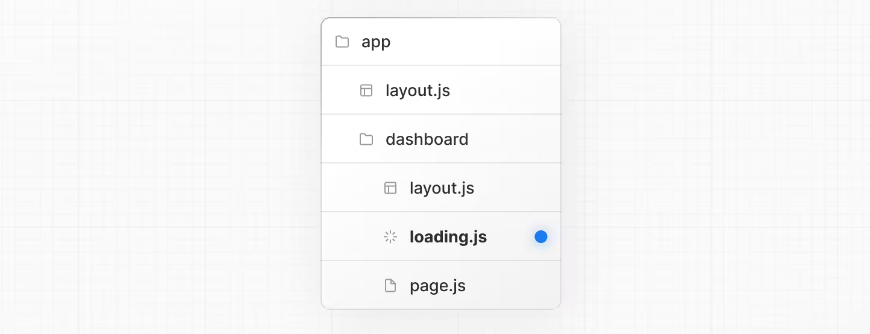
Create a loading state by adding a loading.js file inside a folder.
在文件夹中添加 loading.js 文件以创建加载状态。
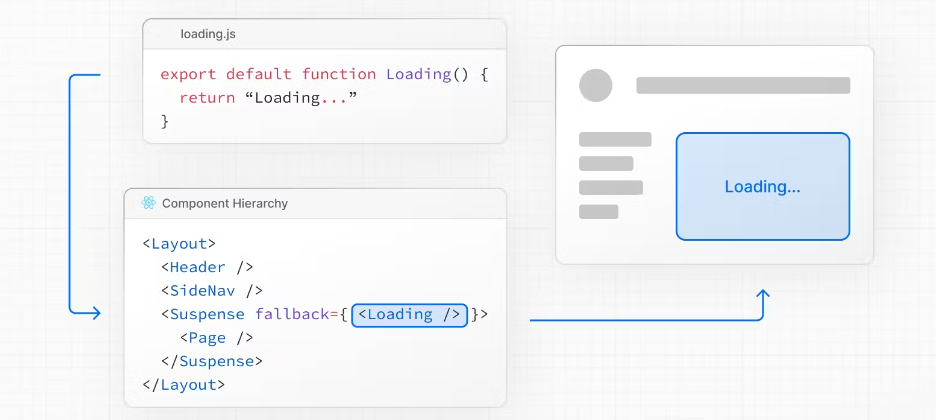
export default function Loading() {
// You can add any UI inside Loading, including a Skeleton.
return <LoadingSkeleton />
}In the same folder, loading.js will be nested inside layout.js. It will automatically wrap the page.js file and any children below in a <Suspense> boundary.
在同一个文件夹中, loading.js 将嵌套在 layout.js 内部。它将自动将 page.js 文件和下面的任何子文件包装在 <Suspense> 边界中。
Good to know: 值得了解:
Navigation is immediate, even with server-centric routing.
即使使用以服务器为中心的路由,导航也是即时的。Navigation is interruptible, meaning changing routes does not need to wait for the content of the route to fully load before navigating to another route.
导航是可以中断的,这意味着更改路由无需等待路由的内容完全加载即可导航到另一个路由。Shared layouts remain interactive while new route segments load.
在加载新的路由段时,共享布局保持交互性。
2.Streaming with Suspense 使用 Suspense 进行流式传输
In addition to loading.js, you can also manually create Suspense Boundaries for your own UI components. The App Router supports streaming with Suspense for both Node.js and Edge runtimes.
除了 loading.js 之外,您还可以为自己的 UI 组件手动创建 Suspense 边界。App Router 支持 Node.js 和 Edge 运行时的 Suspense 流式传输。
a.What is Streaming? 什么是流式传输?
To learn how Streaming works in React and Next.js, it's helpful to understand Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and its limitations.
要了解 Streaming 在 React 和 Next.js 中的工作原理,了解服务器端渲染 (SSR) 及其局限性会有所帮助。
With SSR, there's a series of steps that need to be completed before a user can see and interact with a page:
使用 SSR,在用户可以看到并与页面互动之前,需要完成一系列步骤:
First, all data for a given page is fetched on the server.
首先,在服务器上获取给定页面的所有数据。
The server then renders the HTML for the page.
然后,服务器呈现页面的 HTML。
The HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for the page are sent to the client.
页面的 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 被发送到客户端。
A non-interactive user interface is shown using the generated HTML, and CSS.
使用生成的 HTML 和 CSS 显示非交互式用户界面。
Finally, React hydrates the user interface to make it interactive.
最后,React 对用户界面进行水合,使其具有交互性。
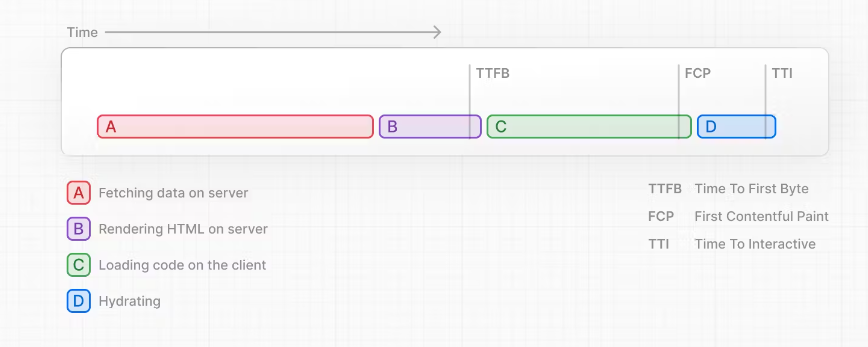
These steps are sequential and blocking, meaning the server can only render the HTML for a page once all the data has been fetched. And, on the client, React can only hydrate the UI once the code for all components in the page has been downloaded.
这些步骤是顺序的且会阻塞,这意味着服务器只能在获取所有数据后才能呈现页面的 HTML。而且,在客户端,React 只能在下载页面中所有组件的代码后才能对 UI 进行水合。
SSR with React and Next.js helps improve the perceived loading performance by showing a non-interactive page to the user as soon as possible.
使用 React 和 Next.js 的 SSR 有助于通过尽快向用户显示非交互式页面来改善感知到的加载性能。
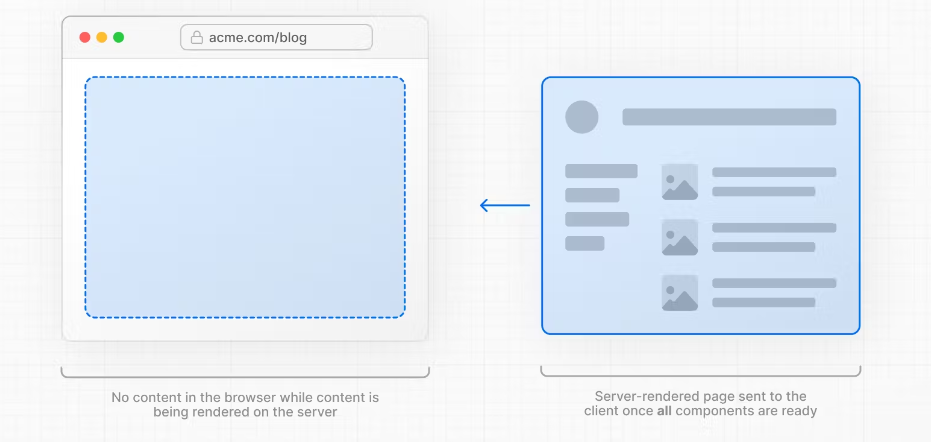
However, it can still be slow as all data fetching on server needs to be completed before the page can be shown to the user.
但是,它仍然可能很慢,因为在页面可以向用户显示之前,需要完成服务器上的所有数据获取。
Streaming allows you to break down the page's HTML into smaller chunks and progressively send those chunks from the server to the client.
流式传输允许您将页面的 HTML 分解为更小的块,并逐步将这些块从服务器发送到客户端。

This enables parts of the page to be displayed sooner, without waiting for all the data to load before any UI can be rendered.
这使得页面的部分内容可以更早地显示,而无需等待所有数据加载才能渲染任何 UI。
Streaming works well with React's component model because each component can be considered a chunk. Components that have higher priority (e.g. product information) or that don't rely on data can be sent first (e.g. layout), and React can start hydration earlier. Components that have lower priority (e.g. reviews, related products) can be sent in the same server request after their data has been fetched.
流式传输与 React 的组件模型配合良好,因为每个组件都可以被视为一个块。具有较高优先级(例如产品信息)或不依赖于数据的组件可以首先发送(例如布局),React 可以更早地开始水合。具有较低优先级(例如评论、相关产品)的组件可以在获取其数据后在同一服务器请求中发送。
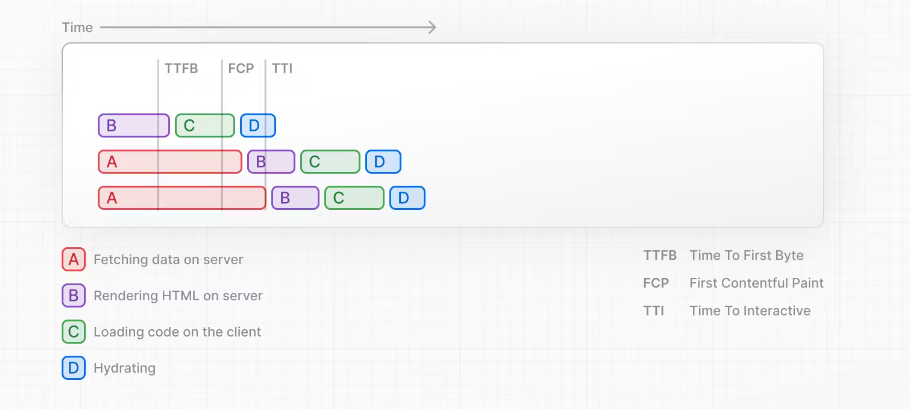
Streaming is particularly beneficial when you want to prevent long data requests from blocking the page from rendering as it can reduce the Time To First Byte (TTFB) and First Contentful Paint (FCP). It also helps improve Time to Interactive (TTI), especially on slower devices.
当您想防止长时间的数据请求阻止页面渲染时,流式传输特别有益,因为它可以减少首次字节时间 (TTFB) 和首次内容绘制 (FCP)。它还有助于改善交互时间 (TTI),尤其是在较慢的设备上。
b.Example 示例
<Suspense> works by wrapping a component that performs an asynchronous action (e.g. fetch data), showing fallback UI (e.g. skeleton, spinner) while it's happening, and then swapping in your component once the action completes.
<Suspense> 通过包装一个执行异步操作(例如获取数据)的组件来工作,在执行操作时显示后备 UI(例如骨架、旋转器),然后在操作完成后将其换成您的组件。
import { Suspense } from 'react'
import { PostFeed, Weather } from './Components'
export default function Posts() {
return (
<section>
<Suspense fallback={<p>Loading feed...</p>}>
<PostFeed />
</Suspense>
<Suspense fallback={<p>Loading weather...</p>}>
<Weather />
</Suspense>
</section>
)
}By using Suspense, you get the benefits of:
通过使用 Suspense,您可以获得以下好处:
Streaming Server Rendering - Progressively rendering HTML from the server to the client.
流式服务器渲染 - 逐步将 HTML 从服务器渲染到客户端。
Selective Hydration - React prioritizes what components to make interactive first based on user interaction.
选择性水合 - React 优先考虑根据用户交互首先使哪些组件具有交互性。
For more Suspense examples and use cases, please see the React Documentation.
有关更多 Suspense 示例和用例,请参阅 React 文档。
c.SEO
Next.js will wait for data fetching inside generateMetadata to complete before streaming UI to the client. This guarantees the first part of a streamed response includes <head> tags.
Next.js 将等待 generateMetadata 中的数据获取完成,然后再将 UI 流式传输到客户端。这保证了流式响应的第一部分包括 <head> 标签。
Since streaming is server-rendered, it does not impact SEO. You can use the Rich Results Test tool from Google to see how your page appears to Google's web crawlers and view the serialized HTML (source).
由于流媒体是服务器渲染的,因此它不会影响 SEO。您可以使用 Google 的富媒体结果测试工具来查看您的页面在 Google 网络抓取工具中的显示方式,并查看序列化的 HTML(来源)。
e.Status Codes 状态代码
When streaming, a 200 status code will be returned to signal that the request was successful.
流式传输时,将返回 200 状态代码以发出请求成功信号。
The server can still communicate errors or issues to the client within the streamed content itself, for example, when using redirect or notFound. Since the response headers have already been sent to the client, the status code of the response cannot be updated. This does not affect SEO.
服务器仍然可以在流式传输内容本身内向客户端传达错误或问题,例如,在使用 redirect 或 notFound 时。由于响应头已发送给客户端,因此无法更新响应的状态代码。这不会影响 SEO。
