Fetching 数据获取
Rendering converts the code you write into user interfaces. React and Next.js allow you to create hybrid web applications where parts of your code can be rendered on the server or the client. This section will help you understand the differences between these rendering environments, strategies, and runtimes.
渲染将您编写的代码转换为用户界面。React 和 Next.js 允许您创建混合 Web 应用程序,其中代码的某些部分可以在服务器或客户端上渲染。本部分将帮助您了解这些渲染环境、策略和运行时之间的差异。
1.Fundamentals 基础知识
To start, it's helpful to be familiar with three foundational web concepts:
首先,熟悉三个基础 Web 概念非常有帮助:
The Environments your application code can be executed in: the server and the client.
您的应用程序代码可以执行的环境:服务器和客户端。The Request-Response Lifecycle that's initiated when a user visits or interacts with your application.
当用户访问或与您的应用程序交互时启动的请求-响应生命周期。The Network Boundary that separates server and client code.
将服务器和客户端代码分隔开的网络边界。
a.Rendering Environments 渲染环境
There are two environments where web applications can be rendered: the client and the server.
Web 应用程序可以在两个环境中呈现:客户端和服务器。
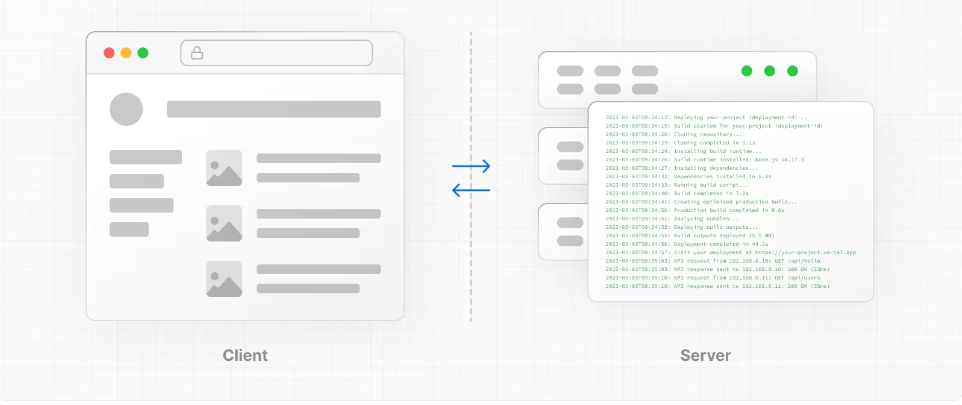
The client refers to the browser on a user's device that sends a request to a server for your application code. It then turns the response from the server into a user interface.
客户端是指用户设备上的浏览器,它向服务器发送请求以获取应用程序代码。然后,它将来自服务器的响应转换为用户界面。The server refers to the computer in a data center that stores your application code, receives requests from a client, and sends back an appropriate response.
服务器是指数据中心中存储您的应用程序代码、接收来自客户端的请求并发送回适当响应的计算机。
Historically, developers had to use different languages (e.g. JavaScript, PHP) and frameworks when writing code for the server and the client. With React, developers can use the same language (JavaScript), and the same framework (e.g. Next.js or your framework of choice). This flexibility allows you to seamlessly write code for both environments without context switching.
过去,开发人员在为服务器和客户端编写代码时必须使用不同的语言(例如 JavaScript、PHP)和框架。使用 React,开发人员可以使用相同的语言(JavaScript)和相同的框架(例如 Next.js 或您选择的框架)。这种灵活性允许您在不切换上下文的情况下无缝地为两种环境编写代码。
However, each environment has its own set of capabilities and constraints. Therefore, the code you write for the server and the client is not always the same. There are certain operations (e.g. data fetching or managing user state) that are better suited for one environment over the other.
但是,每种环境都有自己的一组功能和约束。因此,您为服务器和客户端编写的代码并不总是相同的。某些操作(例如数据获取或管理用户状态)更适合一种环境而不是另一种环境。
Understanding these differences is key to effectively using React and Next.js. We'll cover the differences and use cases in more detail on the Server and Client Components pages, for now, let's continue building on our foundation.
了解这些差异是有效使用 React 和 Next.js 的关键。我们将在服务器和客户端组件页面中更详细地介绍差异和用例,现在,让我们继续构建我们的基础。
b.Request-Response Lifecycle 请求-响应生命周期
Broadly speaking, all websites follow the same Request-Response Lifecycle:
从广义上讲,所有网站都遵循相同的请求-响应生命周期:
Ⅰ.User Action: The user interacts with a web application. This could be clicking a link, submitting a form, or typing a URL directly into the browser's address bar.
用户操作:用户与 Web 应用程序交互。这可能是单击链接、提交表单或直接在浏览器的地址栏中键入 URL。
Ⅱ.HTTP Request: The client sends an HTTP request to the server that contains necessary information about what resources are being requested, what method is being used (e.g. GET, POST), and additional data if necessary.
HTTP 请求:客户端向服务器发送一个 HTTP 请求,其中包含有关请求的资源、正在使用的方法(例如 GET 、 POST )以及必要时的其他数据。
Ⅲ.Server: The server processes the request and responds with the appropriate resources. This process may take a couple of steps like routing, fetching data, etc.
服务器:服务器处理请求并使用适当的资源进行响应。此过程可能需要执行路由、获取数据等几个步骤。
Ⅳ.HTTP Response: After processing the request, the server sends an HTTP response back to the client. This response contains a status code (which tells the client whether the request was successful or not) and requested resources (e.g. HTML, CSS, JavaScript, static assets, etc).
HTTP 响应:在处理请求后,服务器将 HTTP 响应发送回客户端。此响应包含一个状态代码(告诉客户端请求是否成功)和请求的资源(例如 HTML、CSS、JavaScript、静态资产等)。
Ⅴ.Client: The client parses the resources to render the user interface.
客户端:客户端解析资源以呈现用户界面。
Ⅵ.User Action: Once the user interface is rendered, the user can interact with it, and the whole process starts again.
用户操作:一旦用户界面被渲染,用户就可以与之交互,整个过程重新开始。
A major part of building a hybrid web application is deciding how to split the work in the lifecycle, and where to place the Network Boundary.
构建混合 Web 应用程序的主要部分是决定如何在生命周期中拆分工作,以及将网络边界放在哪里。
c.Network Boundary 网络边界
In web development, the Network Boundary is a conceptual line that separates the different environments. For example, the client and the server, or the server and the data store.
在 Web 开发中,网络边界是一个将不同环境分隔开来的概念性界限。例如,客户端和服务器,或服务器和数据存储。
In React, you choose where to place the client-server network boundary wherever it makes the most sense.
在 React 中,您可以选择将客户端-服务器网络边界放在最合理的位置。
Behind the scenes, the work is split into two parts: the client module graph and the server module graph. The server module graph contains all the components that are rendered on the server, and the client module graph contains all components that are rendered on the client.
在幕后,工作被分成两部分:客户端模块图和服务器模块图。服务器模块图包含所有在服务器上呈现的组件,而客户端模块图包含所有在客户端上呈现的组件。
It may be helpful to think about module graphs as a visual representation of how files in your application depend on each other.
将模块图视为应用程序中的文件如何相互依赖的可视化表示可能会有所帮助。
You can use the React "use client" convention to define the boundary. There's also a "use server" convention, which tells React to do some computational work on the server.
您可以使用 React "use client" 约定来定义边界。还有一个 "use server" 约定,它告诉 React 在服务器上执行一些计算工作。
2.Building Hybrid Applications 构建混合应用程序
When working in these environments, it's helpful to think of the flow of the code in your application as unidirectional. In other words, during a response, your application code flows in one direction: from the server to the client.
在这些环境中工作时,将应用程序中的代码流视为单向流很有帮助。换句话说,在响应期间,应用程序代码按一个方向流动:从服务器到客户端。
If you need to access the server from the client, you send a new request to the server rather than re-use the same request. This makes it easier to understand where to render your components and where to place the Network Boundary.
如果您需要从客户端访问服务器,则向服务器发送一个新请求,而不是重复使用相同的请求。这使得更容易理解在何处呈现组件以及在何处放置网络边界。
In practice, this model encourages developers to think about what they want to execute on the server first, before sending the result to the client and making the application interactive.
在实践中,此模型鼓励开发人员在将结果发送到客户端并使应用程序具有交互性之前,先考虑要在服务器上执行什么。
This concept will become clearer when we look at how you can interleave client and server components in the same component tree.
当我们研究如何在同一组件树中交错客户端和服务器组件时,这个概念会变得更加清晰。
