Patterns and Best Practices 模式和最佳实践
There are a few recommended patterns and best practices for fetching data in React and Next.js. This page will go over some of the most common patterns and how to use them.
在 React 和 Next.js 中获取数据有一些推荐的模式和最佳实践。此页面将介绍一些最常见的模式以及如何使用它们。
1.Fetching data on the server 在服务器上获取数据
Whenever possible, we recommend fetching data on the server with Server Components. This allows you to:
只要有可能,我们建议使用服务器组件在服务器上获取数据。这使您可以:
Have direct access to backend data resources (e.g. databases).
直接访问后端数据资源(例如数据库)。Keep your application more secure by preventing sensitive information, such as access tokens and API keys, from being exposed to the client.
通过防止敏感信息(例如访问令牌和 API 密钥)暴露给客户端,让您的应用程序更安全。Fetch data and render in the same environment. This reduces both the back-and-forth communication between client and server, as well as the work on the main thread on the client.
在同一环境中获取数据并呈现。这减少了客户端和服务器之间的往返通信,以及客户端上的主线程上的工作。Perform multiple data fetches with single round-trip instead of multiple individual requests on the client.
使用单次往返执行多个数据获取,而不是在客户端上进行多个单独的请求。Reduce client-server waterfalls.
减少客户端-服务器瀑布。Depending on your region, data fetching can also happen closer to your data source, reducing latency and improving performance.
根据您的区域,数据获取也可以更靠近您的数据源,从而减少延迟并提高性能。
Then, you can mutate or update data with Server Actions.
然后,您可以使用服务器操作来更改或更新数据。
2.Fetching data where it's needed 在需要的地方获取数据
If you need to use the same data (e.g. current user) in multiple components in a tree, you do not have to fetch data globally, nor forward props between components. Instead, you can use fetch or React cache in the component that needs the data without worrying about the performance implications of making multiple requests for the same data.
如果您需要在树中的多个组件中使用相同的数据(例如当前用户),则不必全局获取数据,也不必在组件之间转发道具。相反,您可以在需要数据的组件中使用 fetch 或 React cache ,而无需担心对相同数据发出多个请求的性能影响。
This is possible because fetch requests are automatically memoized. Learn more about request memoization
这是可能的,因为 fetch 请求会自动记忆。了解有关请求记忆的更多信息
Good to know: This also applies to layouts, since it's not possible to pass data between a parent layout and its children.
了解这一点很重要:这也适用于布局,因为无法在父布局及其子布局之间传递数据。
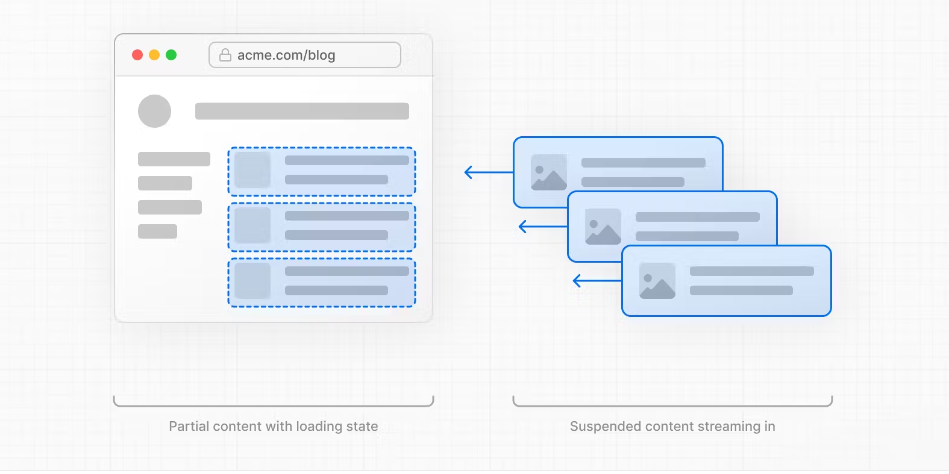
3.Streaming 流媒体
Streaming and Suspense are React features that allow you to progressively render and incrementally stream rendered units of the UI to the client.
流式传输和悬念是 React 的功能,允许您逐步呈现和增量流式传输呈现的 UI 单元到客户端。
With Server Components and nested layouts, you're able to instantly render parts of the page that do not specifically require data, and show a loading state for parts of the page that are fetching data. This means the user does not have to wait for the entire page to load before they can start interacting with it.
借助服务器组件和嵌套布局,您可以立即呈现页面中不需要特定数据的部分,并为正在获取数据的页面部分显示加载状态。这意味着用户不必等到整个页面加载完毕即可开始与之交互。
4.Parallel and sequential data fetching 并行和顺序数据获取
When fetching data inside React components, you need to be aware of two data fetching patterns: Parallel and Sequential.
在 React 组件中获取数据时,您需要了解两种数据获取模式:并行和顺序。
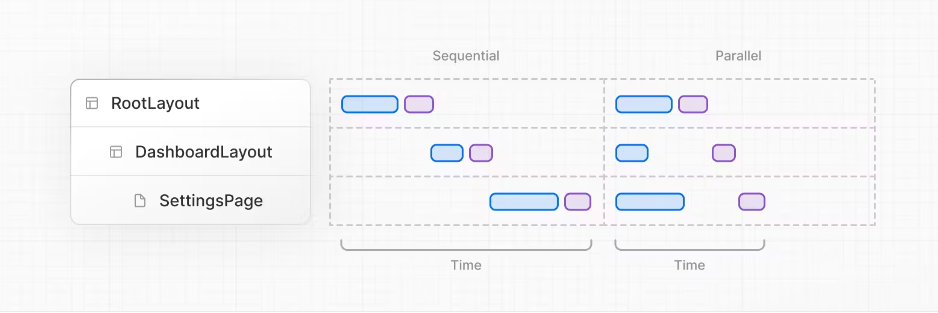
With sequential data fetching, requests in a route are dependent on each other and therefore create waterfalls. There may be cases where you want this pattern because one fetch depends on the result of the other, or you want a condition to be satisfied before the next fetch to save resources. However, this behavior can also be unintentional and lead to longer loading times.
使用顺序数据提取时,路由中的请求相互依赖,因此会创建瀑布。在某些情况下,您可能需要这种模式,因为一个提取依赖于另一个提取的结果,或者您希望在下一个提取之前满足某个条件以节省资源。但是,此行为也可能是无意的,并导致更长的加载时间。With parallel data fetching, requests in a route are eagerly initiated and will load data at the same time. This reduces client-server waterfalls and the total time it takes to load data.
通过并行数据获取,路由中的请求会被立即启动,并且会同时加载数据。这减少了客户端-服务器瀑布和加载数据所需的总时间。
a.Sequential Data Fetching 顺序数据获取
If you have nested components, and each component fetches its own data, then data fetching will happen sequentially if those data requests are different (this doesn't apply to requests for the same data as they are automatically memoized).
如果您有嵌套组件,并且每个组件获取自己的数据,那么如果这些数据请求不同,则数据获取将按顺序发生(这不适用于对相同数据的请求,因为它们会自动记忆)。
For example, the Playlists component will only start fetching data once the Artist component has finished fetching data because Playlists depends on the artistID prop:
例如, Playlists 组件只有在 Artist 组件完成数据获取后才会开始获取数据,因为 Playlists 依赖于 artistID 属性:
// app/artist/[username]/page.tsx
// ...
async function Playlists({ artistID }: { artistID: string }) {
// Wait for the playlists
const playlists = await getArtistPlaylists(artistID)
return (
<ul>
{playlists.map((playlist) => (
<li key={playlist.id}>{playlist.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
)
}
export default async function Page({
params: { username },
}: {
params: { username: string }
}) {
// Wait for the artist
const artist = await getArtist(username)
return (
<>
<h1>{artist.name}</h1>
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<Playlists artistID={artist.id} />
</Suspense>
</>
)
}In cases like this, you can use loading.js (for route segments) or React <Suspense> (for nested components) to show an instant loading state while React streams in the result.
在这种情况下,您可以使用 loading.js (对于路由片段)或 React <Suspense> (对于嵌套组件)来显示即时加载状态,而 React 会流式传输结果。
ps: loading的别样用法
This will prevent the whole route from being blocked by data fetching, and the user will be able to interact with the parts of the page that are not blocked.
这将防止整个路由被数据获取阻塞,并且用户将能够与页面上未被阻塞的部分进行交互。
Blocking Data Requests: 阻止数据请求:
An alternative approach to prevent waterfalls is to fetch data globally, at the root of your application, but this will block rendering for all route segments beneath it until the data has finished loading. This can be described as "all or nothing" data fetching. Either you have the entire data for your page or application, or none.
另一种防止瀑布流的方法是在应用程序的根目录全局获取数据,但这会阻塞数据加载完成之前其下方的所有路由段的渲染。这可以描述为“全有或全无”数据获取。您要么拥有整个页面或应用程序的数据,要么一个都没有。
Any fetch requests with await will block rendering and data fetching for the entire tree beneath it, unless they are wrapped in a <Suspense> boundary or loading.js is used. Another alternative is to use parallel data fetching or the preload pattern.
任何带有 await 的获取请求都会阻塞其下整棵树的渲染和数据获取,除非它们被包装在 <Suspense> 边界中或使用了 loading.js 。另一种替代方法是使用并行数据获取或预加载模式。
b.Parallel Data Fetching 并行数据获取
To fetch data in parallel, you can eagerly initiate requests by defining them outside the components that use the data, then calling them from inside the component. This saves time by initiating both requests in parallel, however, the user won't see the rendered result until both promises are resolved.
要并行获取数据,您可以通过在使用数据的组件外部定义请求,然后在组件内部调用它们来急切地启动请求。这通过并行启动两个请求来节省时间,但是,用户在两个 Promise 都解决之前看不到呈现的结果。
In the example below, the getArtist and getArtistAlbums functions are defined outside the Page component, then called inside the component, and we wait for both promises to resolve:
在下面的示例中, getArtist 和 getArtistAlbums 函数在 Page 组件外部定义,然后在组件内部调用,我们等待两个 Promise 都解决:
// app/artist/[username]/page.tsx
import Albums from './albums'
async function getArtist(username: string) {
const res = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/artist/${username}`)
return res.json()
}
async function getArtistAlbums(username: string) {
const res = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/artist/${username}/albums`)
return res.json()
}
export default async function Page({
params: { username },
}: {
params: { username: string }
}) {
// Initiate both requests in parallel
const artistData = getArtist(username)
const albumsData = getArtistAlbums(username)
// Wait for the promises to resolve
const [artist, albums] = await Promise.all([artistData, albumsData])
return (
<>
<h1>{artist.name}</h1>
<Albums list={albums}></Albums>
</>
)
}5.Preloading Data 预加载数据
Another way to prevent waterfalls is to use the preload pattern. You can optionally create a preload function to further optimize parallel data fetching. With this approach, you don't have to pass promises down as props. The preload function can also have any name as it's a pattern, not an API.
防止瀑布流的另一种方法是使用预加载模式。您可以选择创建一个 preload 函数来进一步优化并行数据获取。使用这种方法,您不必将 Promise 作为道具传递。 preload 函数也可以具有任何名称,因为它是一种模式,而不是 API。
// components/Item.tsx
import { getItem } from '@/utils/get-item'
export const preload = (id: string) => {
// void evaluates the given expression and returns undefined
// https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/void
void getItem(id)
}
export default async function Item({ id }: { id: string }) {
const result = await getItem(id)
// ...
}// app/item/[id]/page.tsx
import Item, { preload, checkIsAvailable } from '@/components/Item'
export default async function Page({
params: { id },
}: {
params: { id: string }
}) {
// starting loading item data
preload(id)
// perform another asynchronous task
const isAvailable = await checkIsAvailable()
return isAvailable ? <Item id={id} /> : null
}a.Using React cache, server-only, and the Preload Pattern 使用 React cache 、 server-only 和预加载模式
You can combine the cache function, the preload pattern, and the server-only package to create a data fetching utility that can be used throughout your app.
您可以结合使用 cache 函数、 preload 模式和 server-only 包来创建一个数据获取实用程序,该实用程序可在整个应用中使用。
// utils/get-item.ts
import { cache } from 'react'
import 'server-only'
export const preload = (id: string) => {
void getItem(id)
}
export const getItem = cache(async (id: string) => {
// ...
})With this approach, you can eagerly fetch data, cache responses, and guarantee that this data fetching only happens on the server.
通过这种方法,您可以急切地获取数据、缓存响应并确保此数据获取仅在服务器上发生。
The utils/get-item exports can be used by Layouts, Pages, or other components to give them control over when an item's data is fetched.
布局、页面或其他组件可以使用 utils/get-item 导出,以便控制何时获取项目数据。
Good to know: 值得了解:
We recommend using the
server-onlypackage to make sure server data fetching functions are never used on the client.
我们建议使用server-only包来确保服务器数据获取函数绝不会在客户端上使用。
6.Preventing sensitive data from being exposed to the client 防止敏感数据暴露给客户端
We recommend using React's taint APIs, taintObjectReference and taintUniqueValue, to prevent whole object instances or sensitive values from being passed to the client.
我们建议使用 React 的污染 API, taintObjectReference 和 taintUniqueValue ,以防止将整个对象实例或敏感值传递给客户端。
To enable tainting in your application, set the Next.js Config experimental.taint option to true:
要在您的应用程序中启用污染,请将 Next.js 配置 experimental.taint 选项设置为 true :
module.exports = {
experimental: {
taint: true,
},
}Then pass the object or value you want to taint to the experimental_taintObjectReference or experimental_taintUniqueValue functions:
然后将您要污染的对象或值传递给 experimental_taintObjectReference 或 experimental_taintUniqueValue 函数:
// app/utils.ts
import { queryDataFromDB } from './api'
import {
experimental_taintObjectReference,
experimental_taintUniqueValue,
} from 'react'
export async function getUserData() {
const data = await queryDataFromDB()
experimental_taintObjectReference(
'Do not pass the whole user object to the client',
data
)
experimental_taintUniqueValue(
"Do not pass the user's phone number to the client",
data,
data.phoneNumber
)
return data
}// app/page.tsx
import { getUserData } from './data'
export async function Page() {
const userData = getUserData()
return (
<ClientComponent
user={userData} // this will cause an error because of taintObjectReference
phoneNumber={userData.phoneNumber} // this will cause an error because of taintUniqueValue
/>
)
}